When using the Android search dialog or search widget, you can provide search suggestions based on recent search queries. For example, if a user previously searched for "puppies," then that query appears as a suggestion once he or she begins typing the same query. Figure 1 shows an example of a search dialog with recent query suggestions.
Before you begin, you need to implement the search dialog or a search widget for basic searches in your application. If you haven't, see Creating a Search Interface .
The Basics
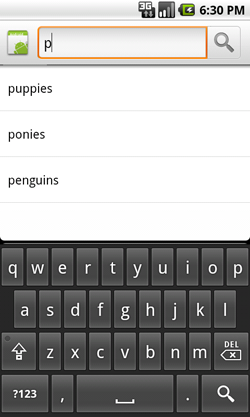
Figure 1. Screenshot of a search dialog with recent query suggestions.
Recent query suggestions are simply saved searches. When the user selects one of
the suggestions, your searchable activity receives a
ACTION_SEARCH
intent with the suggestion as the search query, which your
searchable activity already handles (as described in
Creating a Search
Interface
).
To provide recent queries suggestions, you need to:
- Implement a searchable activity, as described in Creating a Search Interface .
-
Create a content provider that extends
SearchRecentSuggestionsProviderand declare it in your application manifest. - Modify the searchable configuration with information about the content provider that provides search suggestions.
- Save queries to your content provider each time a search is executed.
Just as the Android system displays the search dialog, it also displays the search suggestions below the dialog or search widget. All you need to do is provide a source from which the system can retrieve suggestions.
When the system identifies that your activity is searchable and provides search suggestions, the following procedure takes place as soon as the user begins typing a query:
- The system takes the search query text (whatever has been typed so far) and performs a query to the content provider that contains your suggestions.
-
Your content provider returns a
Cursorthat points to all suggestions that match the search query text. - The system displays the list of suggestions provided by the Cursor.
Once the recent query suggestions are displayed, the following might happen:
- If the user types another key, or changes the query in any way, the aforementioned steps are repeated and the suggestion list is updated.
-
If the user executes the search, the suggestions are ignored and the search is delivered
to your searchable activity using the normal
ACTION_SEARCHintent. -
If the user selects a suggestion, an
ACTION_SEARCHintent is delivered to your searchable activity using the suggested text as the query.
The
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider
class that
you extend for your content provider automatically does the work described above, so there's
actually very little code to write.
Creating a Content Provider
The content provider that you need for recent query suggestions must be an implementation
of
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider
. This class does practically everything
for you. All you have to do is write a class constructor that executes one line of code.
For example, here's a complete implementation of a content provider for recent query suggestions:
public class MySuggestionProvider extends SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider {
public final static String AUTHORITY = "com.example.MySuggestionProvider";
public final static int MODE = DATABASE_MODE_QUERIES;
public MySuggestionProvider() {
setupSuggestions(AUTHORITY, MODE);
}
}
The call to
setupSuggestions()
passes the name of the search authority and a
database mode. The search authority can be any unique string, but the best practice is to use a
fully qualified name for your content provider
(package name followed by the provider's class name; for example,
"com.example.MySuggestionProvider"). The database mode must include
DATABASE_MODE_QUERIES
and can optionally include
DATABASE_MODE_2LINES
, which adds another column
to the suggestions table that allows you to provide a second line of text with each suggestion. For
example, if you want to provide two lines in each suggestion:
public final static int MODE = DATABASE_MODE_QUERIES | DATABASE_MODE_2LINES;
Now declare the content provider in your application manifest with the same authority
string used in your
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider
class (and in the
searchable configuration). For example:
<application>
<provider android:name=".MySuggestionProvider"
android:authorities="com.example.MySuggestionProvider" />
...
</application>
Modifying the Searchable Configuration
To configure the system to use your suggestions provider, you need to add
the
android:searchSuggestAuthority
and
android:searchSuggestSelection
attributes to
the
<searchable>
element in your searchable configuration file. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="com.example.MySuggestionProvider"
android:searchSuggestSelection=" ?"
>
</searchable>
The value for
android:searchSuggestAuthority
should be a fully qualified name for
your content provider that exactly matches the authority used in the content provider (the
AUTHORITY
string in the above example).
The value for
android:searchSuggestSelection
must be a single question mark, preceded by
a space (
" ?"
), which is simply a placeholder for the SQLite selection argument (which is
automatically replaced by the query text entered by the user).
Saving Queries
To populate your collection of recent queries, add each query
received by your searchable activity to your
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider
. To do this, create an instance of
SearchRecentSuggestions
and call
saveRecentQuery()
each time
your searchable activity receives a query. For example, here's how you can save the query during
your activity's
onCreate()
method:
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (Intent.ACTION_SEARCH.equals(intent.getAction())) {
String query = intent.getStringExtra(SearchManager.QUERY);
SearchRecentSuggestions suggestions = new SearchRecentSuggestions(this,
MySuggestionProvider.AUTHORITY, MySuggestionProvider.MODE);
suggestions.saveRecentQuery(query, null);
}
}
The
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider
constructor requires the
same authority and database mode declared by your content provider.
The
saveRecentQuery()
method takes
the search query string as the first parameter and, optionally, a second string to include as the
second line of the suggestion (or null). The second parameter is only used if you've enabled
two-line mode for the search suggestions with
DATABASE_MODE_2LINES
. If you have enabled
two-line mode, then the query text is also matched against this second line when the system
looks for matching suggestions.
Clearing the Suggestion Data
To protect the user's privacy, you should always provide a way for the user to clear the recent
query suggestions. To clear the query history, call
clearHistory()
. For example:
SearchRecentSuggestions suggestions = new SearchRecentSuggestions(this,
HelloSuggestionProvider.AUTHORITY, HelloSuggestionProvider.MODE);
suggestions.clearHistory();
Execute this from your choice of a "Clear Search History" menu item, preference item, or button. You should also provide a confirmation dialog to verify that the user wants to delete their search history.