This page describes several common database administration and reporting tools that you can use to connect to your Google Cloud SQL instances.
Contents
- Overview
- Connecting with MySQL Workbench
- Connecting with Toad for MySQL
- Connecting with SQuirrel SQL
Overview
Database administration and reporting tools provide varying degrees of support for managing your database. Select a tool based on what type of administration and reporting you need to do. For example, if you need to connect to one database and issue a few SQL commands, consider using MySQL client (see Connecting with MySQL Client ). If you need to design or manage many databases simultaneously, then use one of the visual-based tools discussed here.
We discuss a limited number of tools in this page, but, if your tool is not shown below, it is likely that you can follow the steps for a tool that is similar and successfully connect.
Connecting with MySQL Workbench
This section shows how to connect to your Google Cloud SQL instance database with MySQL Workbench . Before connecting, make sure you have assigned an IP address to your instance and the instance will accept connections from the IP address where you are running the tool (see Configuring access for non-App Engine applications ).
- In the MySQL Workbench home view, click New Connection .
-
In the
Setup New Connection
window, provide a
Connection Name
,
Hostname
,
Username
, and
Default Schema
, if applicable,
as show in Figure 1.
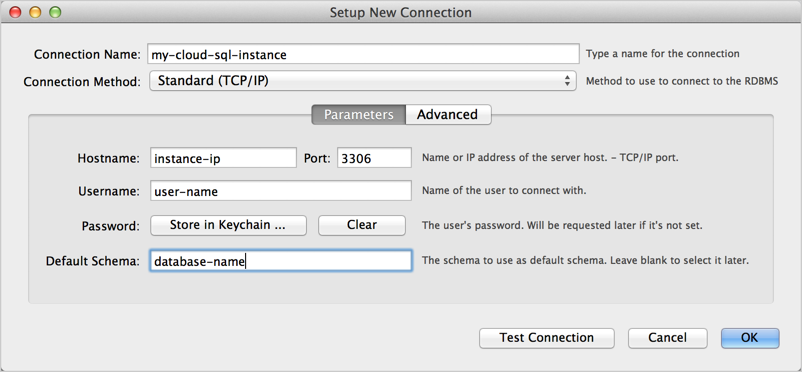
Figure 1: Specifying parameters in the MySQL Workbench Setup New Connection window. - Click Test Connection . You will be prompted for a password.
-
Optionally, click
Advanced
, and fill in the information
for connecting with SSL as shown in Figure 2. Be sure to select
Use SSL if available
and specify a
SSL CA File
,
a
SSL CERT File
, and a
SSL key File
.
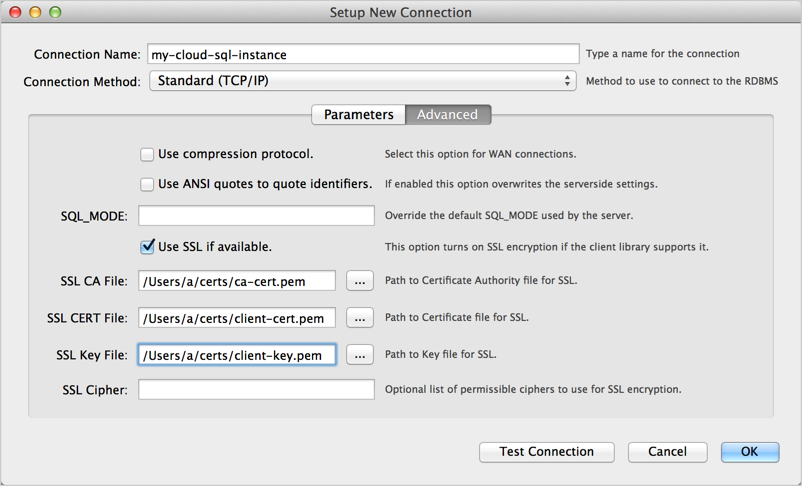
Figure 2: Specifying advanced options in the MySQL Workbench Setup New Connection window. - Click Test Connection to make sure all the advanced parameters are okay.
- Click Close .
- Connect with the connection you just created.
-
Once connected, you can test if you are using SSL by executing the following
SQL statement:
SHOW STATUS like 'ssl_cipher';
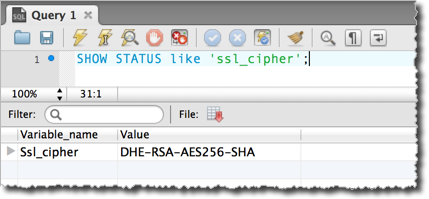
Figure 3: Testing if the MySQL Workbench connection uses SSL.
Connecting with Toad for MySQL
This section shows how to connect to your Google Cloud SQL instance database with Toad for MySQL . Before connecting, make sure you have assigned an IP address to your instance and the instance will accept connections from the IP address where you are running the tool (see Configuring access for non-App Engine applications ).
- In Toad for MySQL, create a new connection.
-
In the
New MySQL Connection
window fill in the
following information:
- User - the name of a user in your MySQL database.
- Password - the password for the specified user.
- Host - the IP address you assigned to your instance. For more information, see Configuring Application Access Control . If you have mapped the IP address to host name for your local server, you can use that in this field.
- Database - the instance database to which to connect.
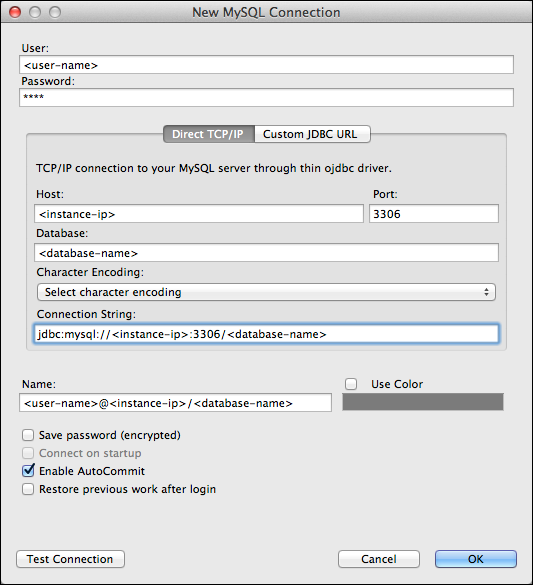
Figure 4: The Create New Connection dialog box in Toad for Mac - Click Test Connection to confirm the connection information is correct.
- Click OK to start the connection.
- In the Enter Password dialog, enter the password for the user. This dialog appears because we did not choose Save password (encrypted) in the Create New Connection dialog.
Configuring Toad to use SSL
In Figure 5, a Create New Connection dialog box is shown with the information for connecting with SSL. Note that not all versions of Toad may support connecting with SSL.
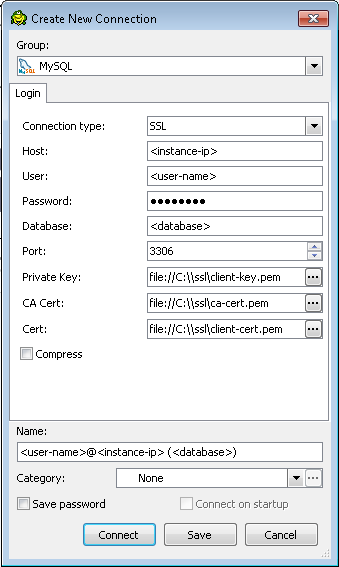
Once connected, you can test if you are using SSL by executing the following
SQL statement and verifying that the
ssl_cipher
value is not empty:
SHOW STATUS like 'ssl_cipher';Back to top
Connecting with SQuirrel SQL
This section shows how to connect to your Google Cloud SQL instance database with SQuirrel SQL . Before connecting, make sure you have assigned an IP address to your instance and the instance will accept connections from the IP address where you are running the tool (see Configuring access for non-App Engine applications ).
- In the SQuirrel SQL client, select the Aliases panel to make it active.
- In the Aliases menu, select New Alias .
-
Fill out the information as shown in Figure 6. Be sure to select then
MySQL Driver and provide values for
<instance-ip>
,
<database>
,
and
<user-name>
.

Figure 6: Configuring a SQuirrel SQL connection to MySQL. - Click Test to test the connection. You will prompted for a password.
- Click OK to save the alias.
- In the Aliases panel, right-click the alias you just created and select Connect .
Configuring SQuirrel SQL to use SSL
This section assumes you have created an SSL certificate (see Configuring SSL for an instance ) and you have three files:
- A CA certificate file, for example, ca-cert.pem .
- A client public key certificate file, for example, client-cert.pem .
- A client private key file, for example, client-key.pem .
Use these files with the instructions Connecting Securely Using SSL , in the MySQL Reference Manual, to create keystore and truststore files. You then need to specify the keystore and truststore files when you start SQuirrel SQL. One way to do this is to edit the script that launches the SQuirrel SQL application as shown below:
$JAVACMD -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=<path-to-keystore> \
-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=<keystore-password> \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=<path-to-truststore> \
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=<truststore-password> \
[existing launch parameters]
After you have started SQuirrel SQL with the valid keystore and truststore information, you can connect with:
jdbc:mysql://<instance-ip>:3306/<database>?verifyServerCertificate=true&useSSL=true&requireSSL=true
Once connected, you can test if you are using SSL by executing the following
SQL statement and verifying that the
ssl_cipher
value is not empty:
SHOW STATUS like 'ssl_cipher';Back to top
