This page discusses how you can use the Google APIs Client Library for Java to send requests to the Google Cloud Storage JSON API.
Specifically, the sample shown here gets metadata about a bucket you specify and lists the objects in the bucket. You can use the general steps shown here to run your own code.
This document assumes that you have Java installed, and you are familiar with Java and the Google Cloud Storage concepts and operations presented in the Getting Started: Using the Developers Console guide.
1. Set up your environment
Set up a directory structure for the project that looks like the following:
. └── src │ └── main │ ├── java │ └── resources
The name of the containing folder (
.
) doesn't matter.
The
java
directory will contain the Java code, and the
resources
directory
will contain client secret information used for authentication.
If you clone the repository that contains the Java sample, the directory structure is created for you:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cloud-storage-docs-json-api-examples.git
2. Create a client secrets file
In the example code, you will use a client secrets file to authenticate with
the Google Cloud Storage JSON API. You can create and download a client secrets (JSON)
file from the Google Developers Console. Rename the file
client_secrets.json
, and put in the
./src/main/resources
folder.
To generate a client secrets file:
- Go to the Google Developers Console .
- Select a project to which the client ID will be associated.
- In the left sidebar, under APIs & AUTH , select Credentials .
- Click Create new Client ID .
- In the Create Client ID window, choose Installed application .
-
Click
Create Client ID
.
The resulting client ID will look like the following example:
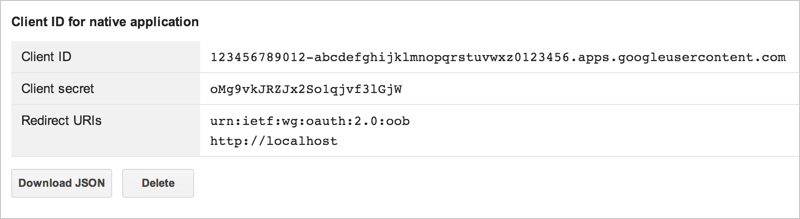
- Click Download JSON .
3. Create your code file
In this step, you will create the Java code file called
StorageSample.java
, and
put it in the
./src/main/java
directory. Copy
the code from below and make the following changes:
-
Set
APPLICATION_NAMEto that identifies your application. -
Set
BUCKET_NAMEto the name of a bucket in the same project as client ID you created.
StorageSample.java
4. Run the sample
Your directory structure at this point should look like this:
. └── src │ └── main │ ├── java │ │ └── StorageSample.java │ └── resources │ └── client_secrets.json
There are a number of ways you can run your sample, for example, with Eclipse , Gradle , or Maven . Here, we'll use a simple Maven setup to run the sample.
To run the sample using Maven:
-
Create a
pom.xmlfile in the root directory and with the contents. If you cloned the respository withgitthen this file already exists. -
Run the following commands from the root directory.
$ mvn compile install $ mvn exec:java
Output from the sample code will be similar to this:
name: example-bucket
location: US
Contents:
timeCreated: 2013-09-03T18:10:46.889Z
owner: {"entity":"group-00b4903a97e991ba23f3f296d7f3e048648a0185d9abfa1e5ce8b0151cdb3353","entityId":"00b4903a97e991ba23f3f296d7f3e048648a0185d9abfa1e5ce8b0151cdb3353"}
object1 (77242 bytes)
object2 (76991 bytes)
...
