This page shows you how to send requests to the Google Cloud Storage using the XML API and a service account to authenticate. A service account is a special account that represents software rather than a person, and is useful for code that interacts with Google Cloud Storage on your behalf.
The first example shows how to create a stand-alone Java program that accesses Google Cloud Storage. The second example shows how to access Google Cloud Storage from within Google App Engine. You can find the code for both samples on GitHub at GoogleCloudPlatform/cloud-storage-docs-xml-api-examples .
Prerequisites
This document assumes:
- You are familiar with Java and the Google Cloud Storage concepts and operations presented in the Hello Google Cloud Storage! guide.
- You are familiar with git and cloning GitHub repositories.
- You have Java and Maven installed.
Command-line example
1. Set up your project
Clone the repository and go to the root of the sample with the following commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cloud-storage-docs-xml-api-examples.git
$ cd cloud-storage-docs-xml-api-examples/storage-serviceaccount-cmdline-sample
2. Create a service account
To create or access an existing service account, see Service Account Authentication . From the Google Developers Console, you will see information for your service account similar to the following example.
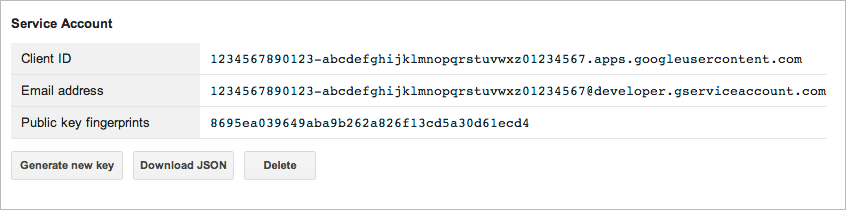
To retrieve the private key (.p12), take one of the following actions:
- If the service account already exists and you have the private key, you can use that key.
- If the service account already exists and you do not have the private key, you can generate a new key and download it. Any applications using the existing private keys associated with this service account will continue to work.
- Create a new service account and download the private key.
You need to put the private key of the service account in the root directory of
the sample. Note that the cloned repository already contains a file named
key.p12
. Rename the key you download to "key.p12" and replace the existing
one.
3. Customize the code
In the
StorageServiceAccountSample.java
code file, do the following:
-
Set the
SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAILto the Email address of the service account. -
Set the
BUCKET_NAMEto the name of a bucket in the same project as the service account.
The key part of the code file is shown below along with buttons that link to the full source code and GitHub project.
StorageServiceAccountSample.java
4. Run the sample
There are a number of ways you can run this sample, for example, with
Eclipse
,
Gradle
, or
Maven
. Here, we'll use Maven. Maven uses
the
pom.xml
file in the root directory of the sample to build the
sample and resolve dependencies.
Run the following commands from the root directory:
$ mvn compile install
$ mvn exec:java
The sample code outputs the contents of a bucket similar to the following output:
Bucket listing for example-bucket:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE ListBucketResult SYSTEM "testing.dtd">
<ListBucketResult xmlns="http://doc.s3.amazonaws.com/2006-03-01">
<Name>example-bucket</Name>
<Prefix/>
<Marker/>
<IsTruncated>false</IsTruncated>
<Contents>
<Key>object</Key>
<Generation>1389398350649000</Generation>
<MetaGeneration>1</MetaGeneration>
<LastModified>2014-01-10T23:59:10.569Z</LastModified>
<ETag>"a5870178133170a8783aaef58ff7c1be"</ETag>
<Size>77242</Size>
<Owner>
<ID>00b4903a972faa8bcce9382576c9129676f1cd6e5def1f5663abbc2ba4625490</ID>
<DisplayName>user name</DisplayName>
</Owner>
</Contents>
...
</ListBucketResult>
App Engine example
1. Set up your project
Clone the repository, change directory to the sample root, and package it with the following commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cloud-storage-docs-xml-api-examples.git
$ cd cloud-storage-docs-xml-api-examples/storage-serviceaccount-appengine-sample
$ mvn clean package
2. Edit the project permissions
This example uses the OAuth 2.0 credentials capabilities of App Engine to generate credentials. You must add the App Engine Service Account Name to the project so that your App Engine application can access your buckets.
To find your App Engine Service Account Name :
- Go to App Engine Console and select your project.
- In the left sidebar, select Application Settings .
- Copy the email address under Service Account Name . It will have the form "[email protected]"
To add the App Engine Service Account Name to your project :
- In the Google Developers Console , select the project that contains the bucket(s) you want to access.
- In the left sidebar, click Permissions .
- Click Add Member .
- In the Email box, enter the Service Account Name of the App Engine application.
- Click Add .
3. Customize the code
Edit the
appengine-web.xml
file to specify the name of your App Engine
application in the
<application/>
tag.
appengine-web.xml
The main class file (
StorageSample.java
) does not require any changes.
The key part of the code file is shown below along with buttons that link to
the full source code and GitHub project.
StorageSample.java
4. Run the sample
There are a number of ways you can run this sample, for example, with
Eclipse
,
Gradle
, or
Maven
. Here, we'll use Maven. The
pom.xml
file contains information about the project, including dependencies
needed to build and run the code.
Use the following command from the root directory of the sample:
$ mvn appengine:update
If this is the first time you have run "update" on the project, a browser window will open prompting you to log in. Log in with the same Google account credentials with which the application is registered.
In a browser go to the App Engine instance. For example, if your App Engine application id is "my-application" and the bucket you want to access is named "bucket-name", then go to:
https://my-application.appspot.com/bucket-name
The result will be a table showing the items in the bucket.
